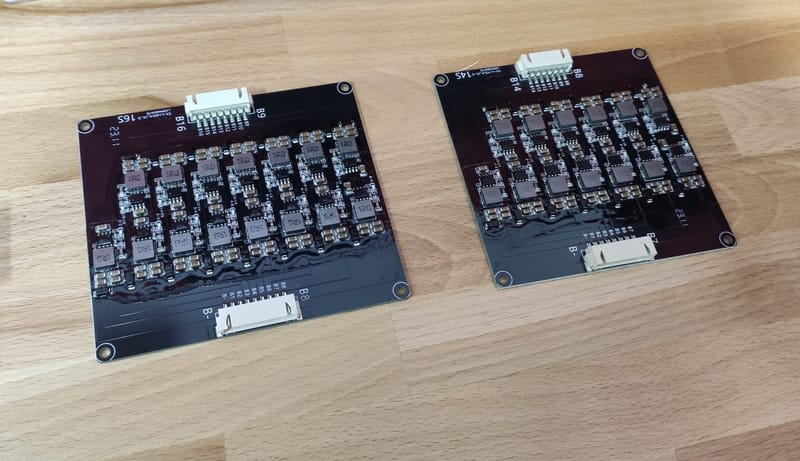
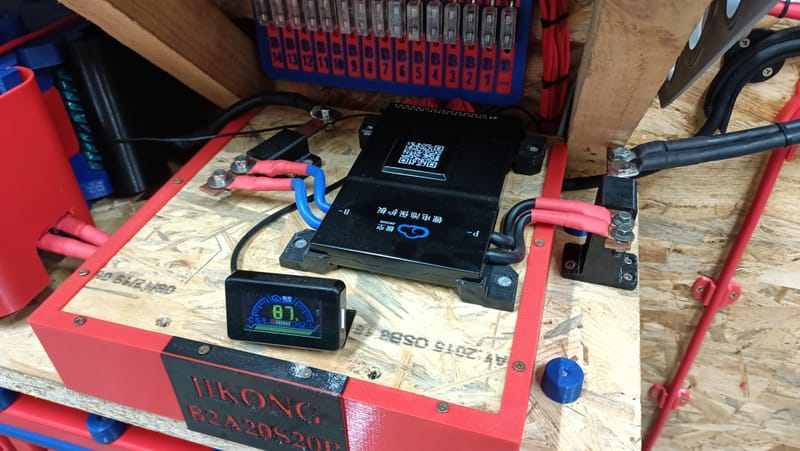
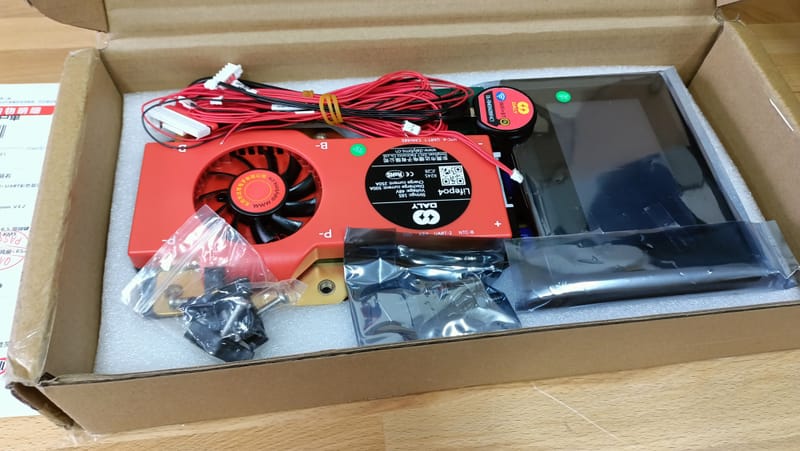
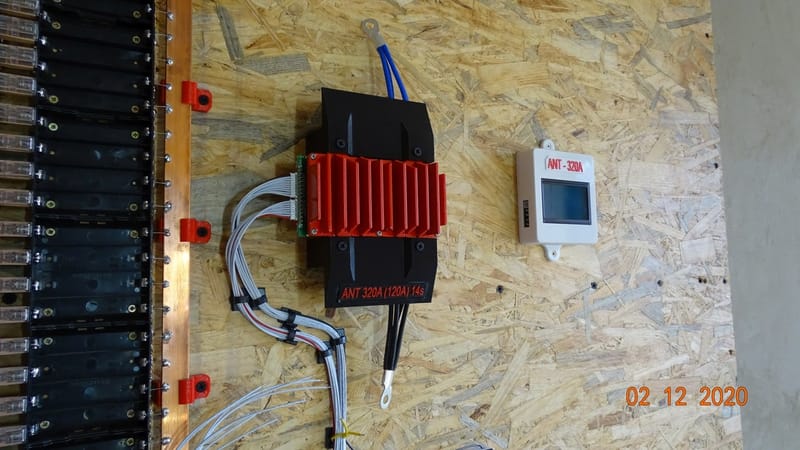
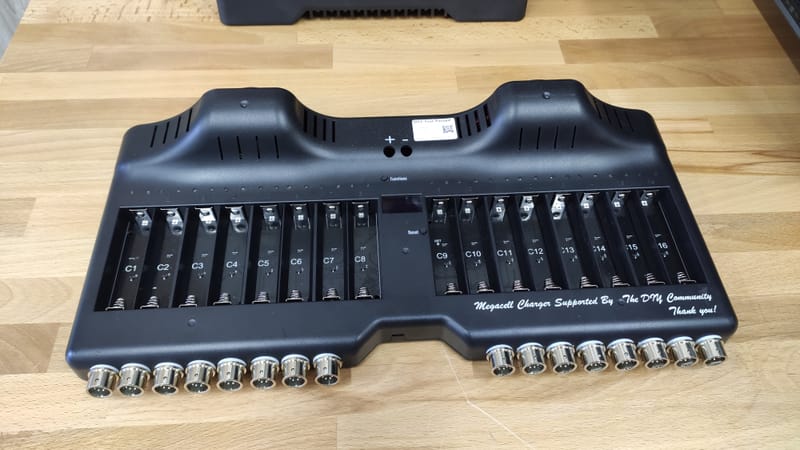
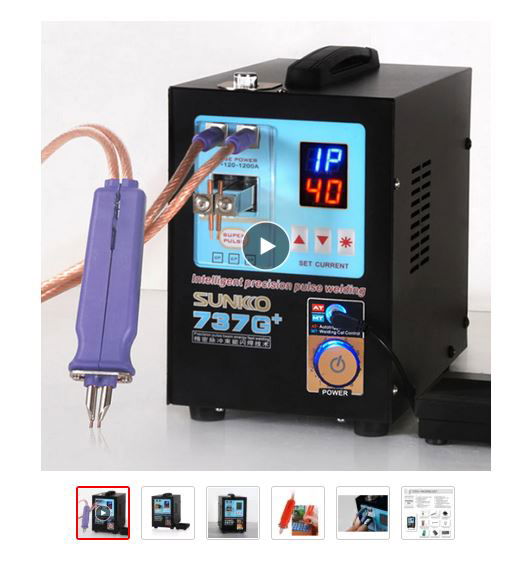
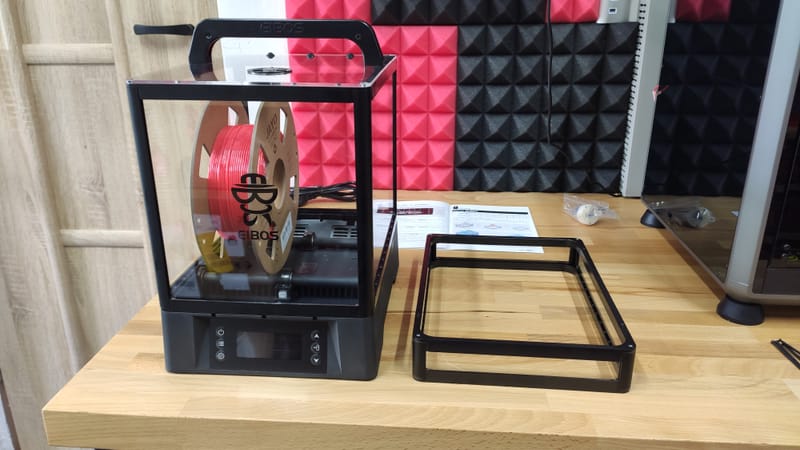
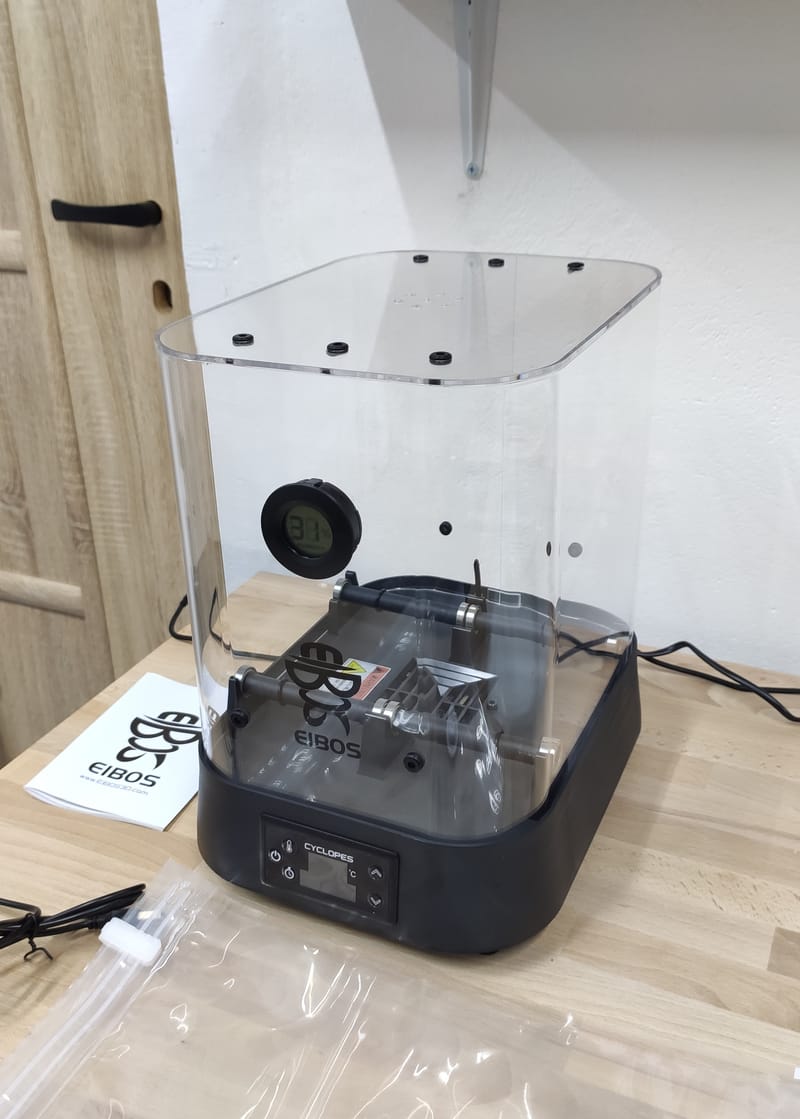
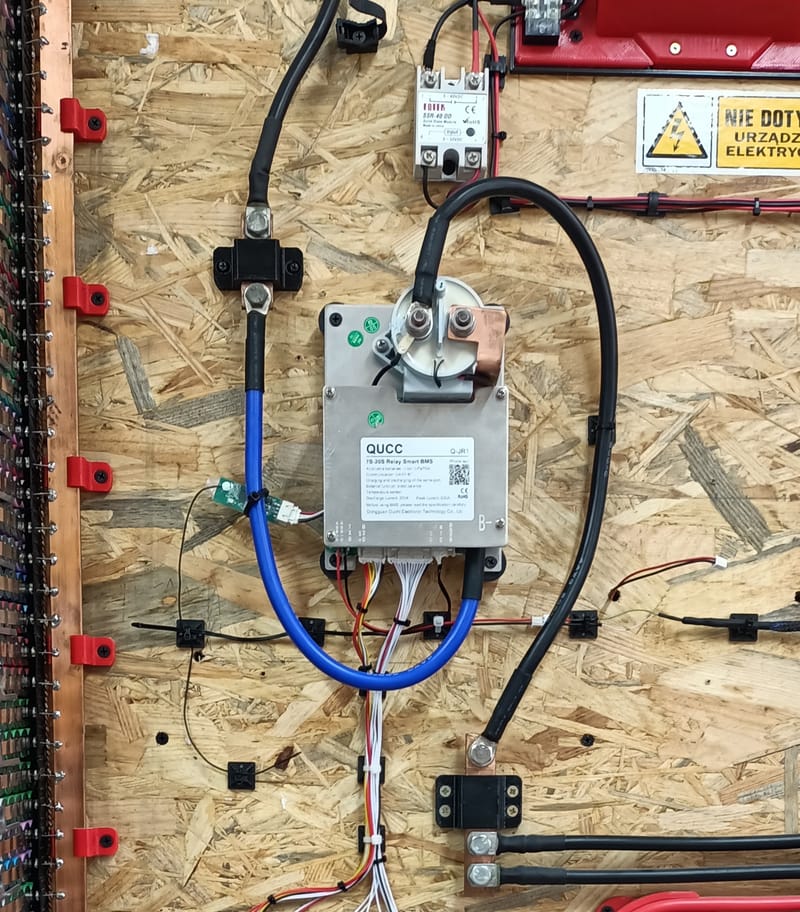
My hobby :)
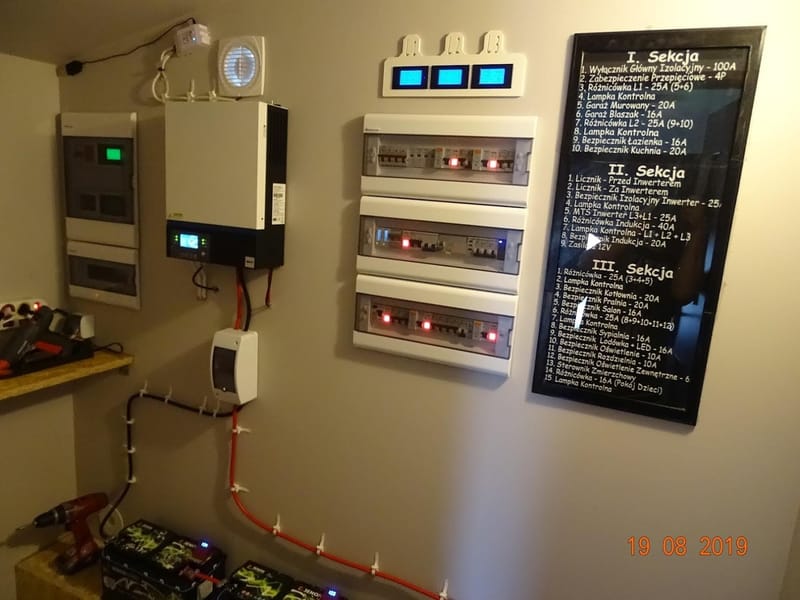
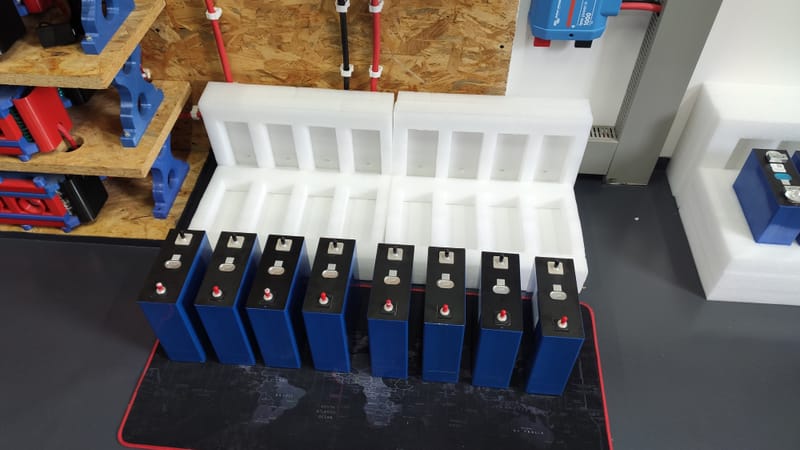
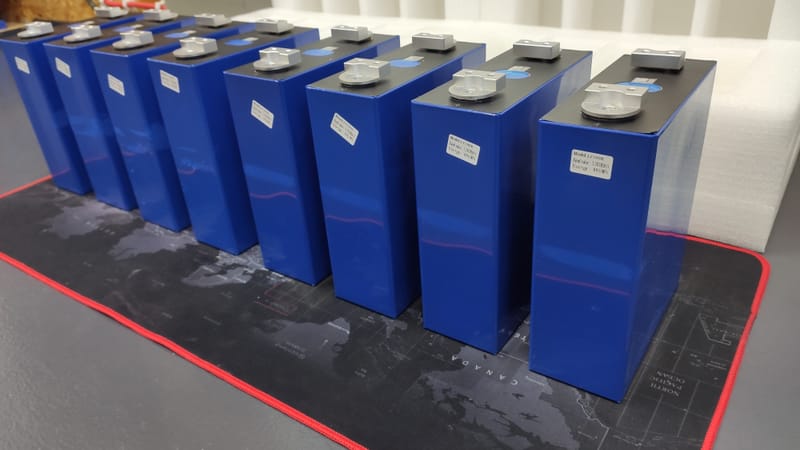
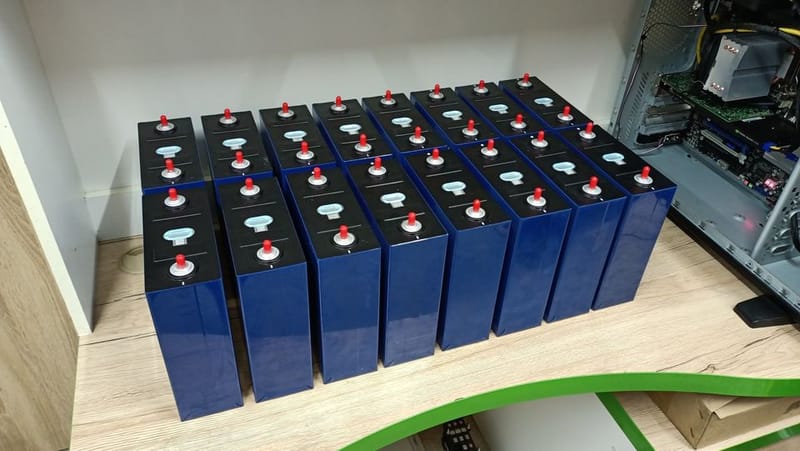
Moje pierwsze zainteresowania tematem zaczęły się od pomysłu na zbudowanie takiego magazynu z ogniw Litowych. Wpadłem na pomysł pozyskiwania ogniw z uszkodzonych bądź nie sprawnych baterii laptopowych i elektronarzędzi, gdyż ogniwa litowe w nich zawarte można przy pewnym nakładzie pracy odzyskać i dać im drugą szansę zanim wylądują w koszu recyklingowym i tak powstał mój pierwszy magazyn :)...
https://youtu.be/sjl4wsU9c0Y
Udało mi się z dużym nakładem pracy i nieocenioną pomocą Żony zbudować Magazyn Energii "PowerWall V1", oraz zarazić innych moim hobby, stworzyłem grupę na FB na która serdecznie zapraszam:
https://www.facebook.com/groups/pw.tech
Powstał również kanał na YouTube poświęcony tematyce DIY czyli Zrób to sam:
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCu4Q6TZcwXy-lU7prYkVZhA
Grupa jak i strona jest w 100% tematyczna, hobbistyczna i nie zajmuje się handlem, jeżeli lubisz zrobić coś sam i nie boisz się pracy, a jednocześnie szukasz informacji w tematyce off-gridu i magazynowania energii jesteś w odpowiednim miejscu :) ...



Support My YT Channel
If you like what I do and think I deserve support, please do :)
Support on the fundraiser
A form of support on Zrzutka, I'm collecting for Tesla reviews :P
Learn MorePhoto Albums
These are photo albums that I share for you related to my hobbies and projects.
Videos On YouTube
I have prepared for you videos from my YT channel arranged in catalogs and playlists, so that it is easier to find interesting information and content.
Facebook groups
I invite you to our FB groups, one dealing with technical topics, the other is a typical stock exchange, when writing posts we stick to the subject of a given group.
CAD projects - STP files
My projects are in STP format, i.e. fully editable. I would like to point out that this is my work, which often lasts many months, which I make available for free and allow for full modification as desired for private use. I also ask you to mark the source, i.e. this page. Support of my work is also welcome :)
Projekty Laser - Pliki DXF
My designs in DXF format, intended for a laser engraver or CNC machine. Support of my work is also welcome :)
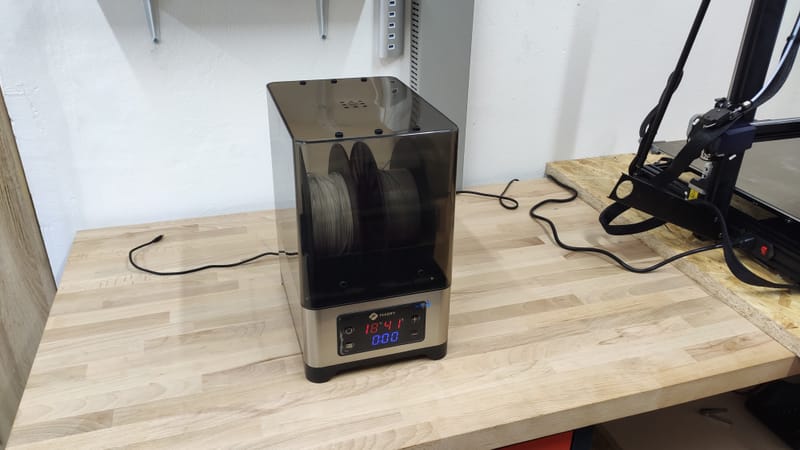
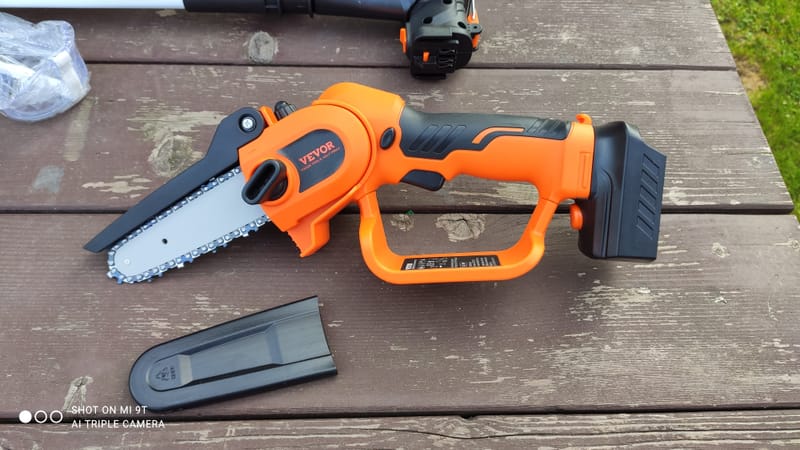
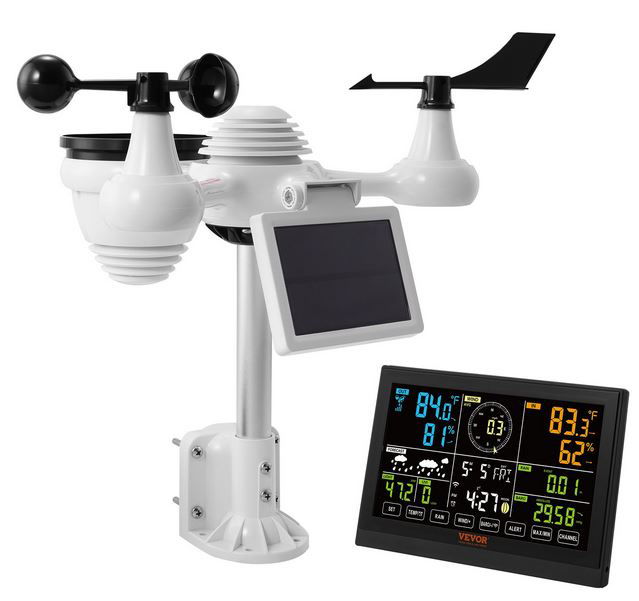
My Devices
Here I put a list of devices that I bought and have some opinion about them. I hope that this opinion and my experience will help you decide whether it is worth buying or not.

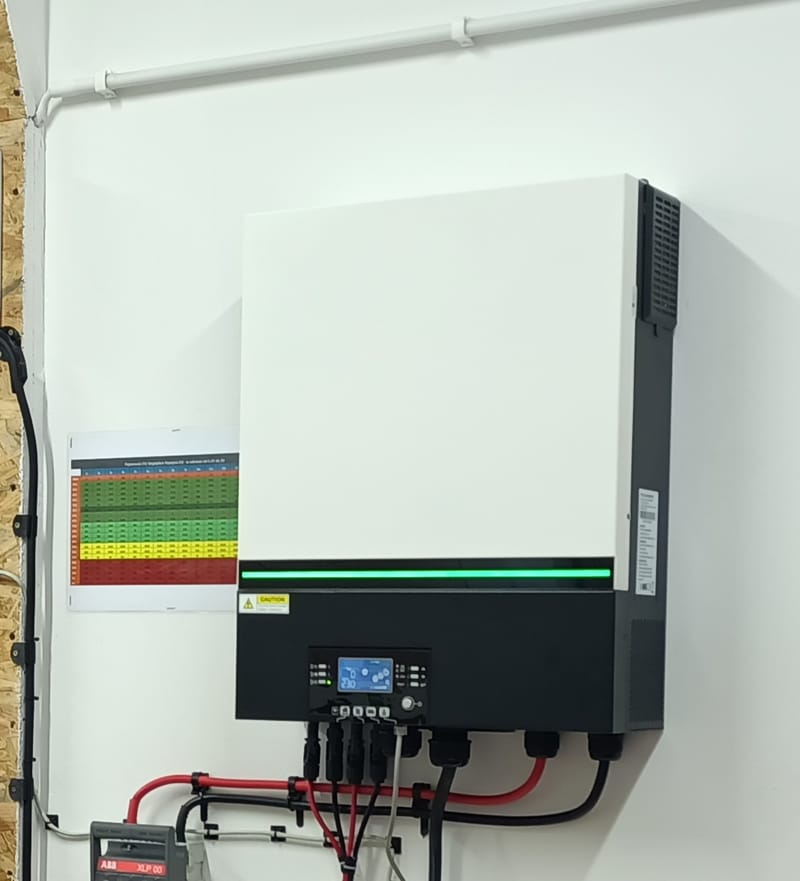
Off-Grid Inverters ANENJI 6.2 kW 48V with WiFi
Off-Grid Inverters ANENJI 6.2 kW 48V with WiFi
Learn More
Off-Grid 48V Axpert MAX II 11kW Twin inverters
Typical Off-Grid 48V Axpert MAX II 11kW Twin inverters
Learn More
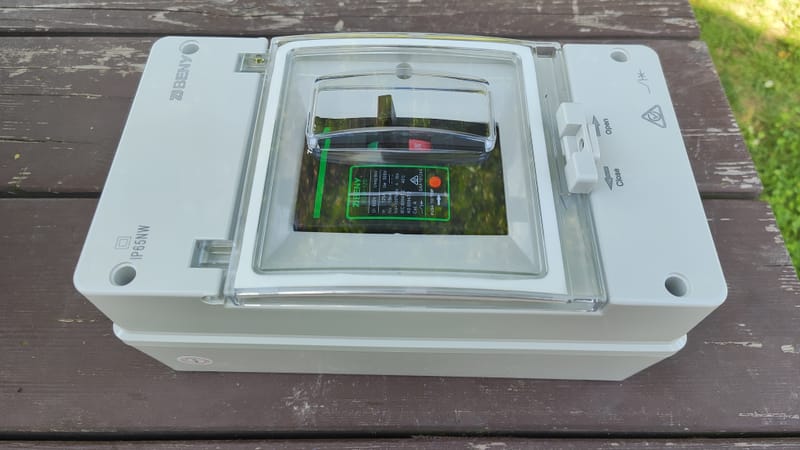
DC protection - PV switchgear
The protections that I use to build the DC switchgear, the main protections from Feeo
Learn More
Elektro-Plast NEOSeries surface-mounted switchgear
Elektro-Plast NEOSeries surface-mounted switchgear
Learn More
GIANTKEY 15A Active Capacitive Balancer
Active Capacitive Balancer, 15A capacity and BT communication.
Learn More
GIANTKEY 4A Active Capacitive Balancer
Active Capacitive Balancer, 4A efficiency and BT communication.
Learn More
Active Capacitive Balancer
Active Capacitive Balancer, one of the most popular devices of this type :)
Learn More
Inverter BMS with Active Balancer JK-PB2A16S20P
Inverter BMS with Active Balancer JK-PB2A16S20P
Learn More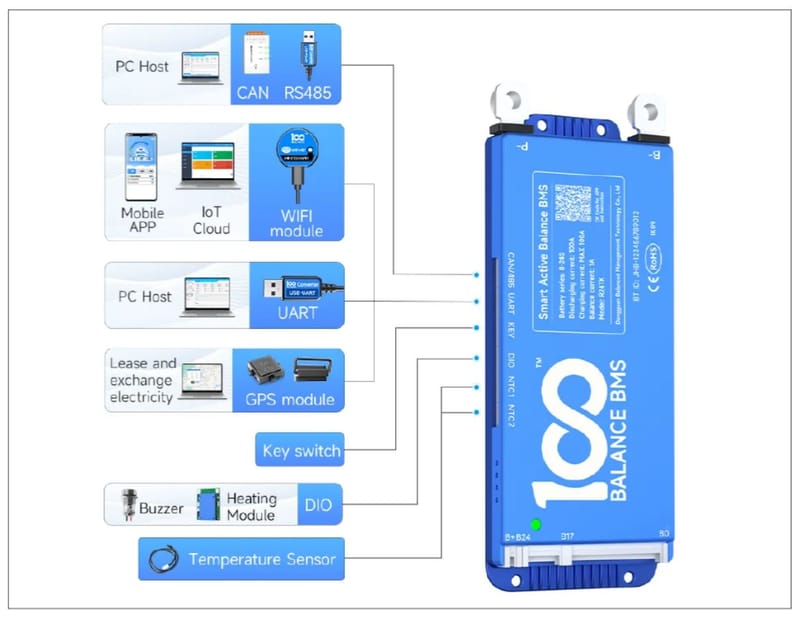
BMS with Active Balancer - 100 Smart Active Balance BMS
BMS with Active Balancer - 100 Smart Active Balance BMS
Learn More
LiFePo4 cells "Aweit Green Energy" EVE V3 LiFePo4 314Ah MB31
LiFePo4 cells "Aweit Green Energy" EVE V3 LiFePo4 314Ah MB31
Learn More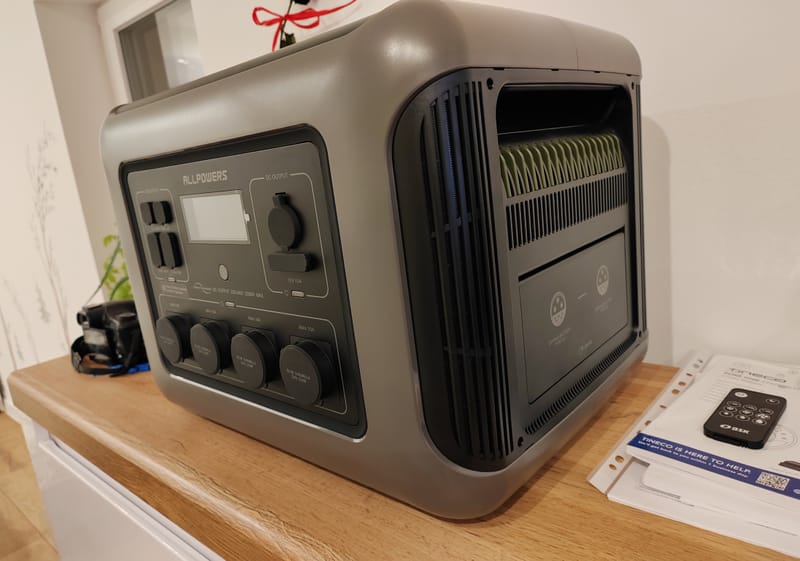
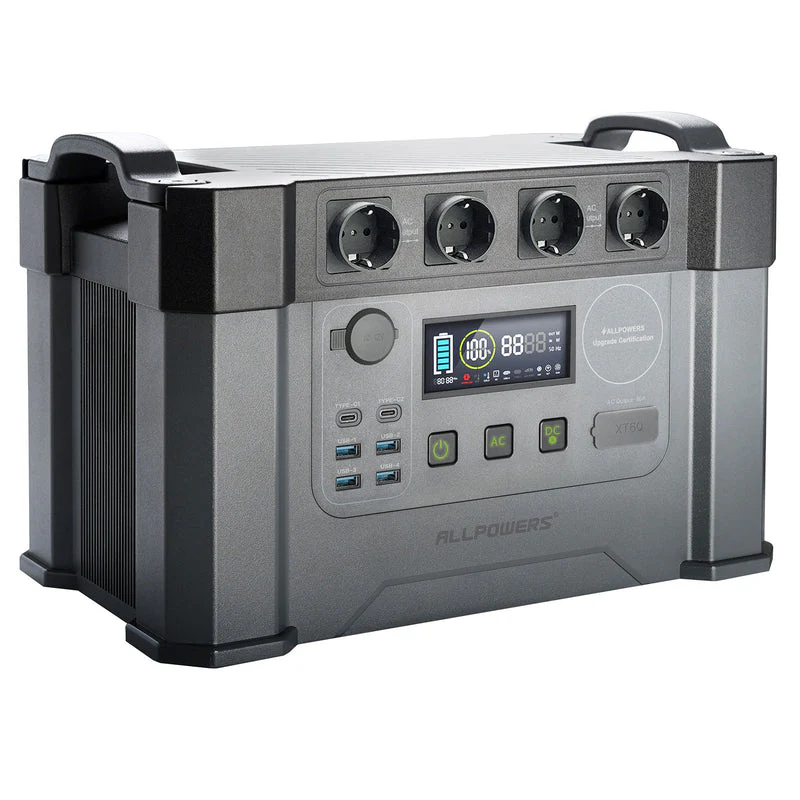
AllPowers R2500 Wifi/BT LFP Portable Power Station
AllPowers R2500 Wifi/BT LFP Portable Power Station
Learn More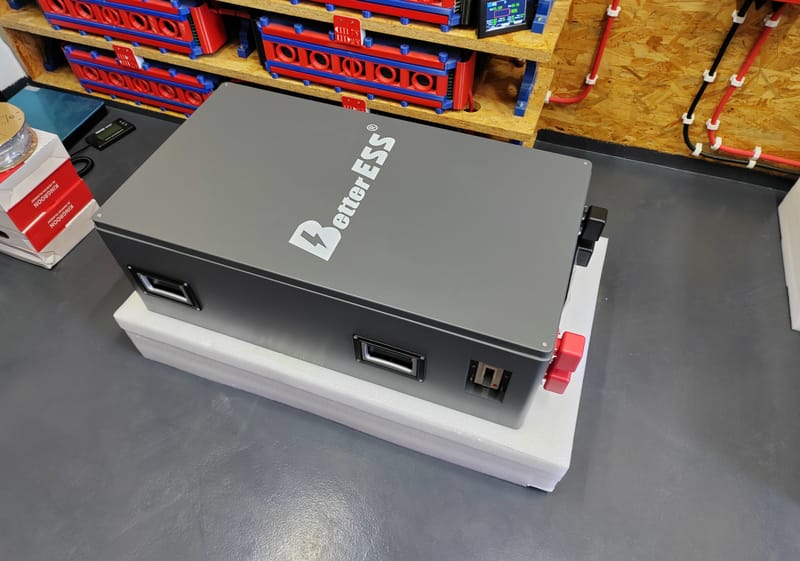
Better ESS - New Version of the LFP 280-314Ah Cell Housing "JKBMS"
Better ESS - New Version of the LFP 280-314Ah Cell Housing "JKBMS"
Learn More
Power Queen 12V 100Ah LiFePo4 battery - Auto-Heating
Power Queen 12V 100Ah LiFePo4 battery - Auto-Heating
Learn More
LiFePo4 cells "Guangdong Tian Qin" EVE V3 LiFePo4 280Ah
LiFePo4 cells "Guangdong Tian Qin" EVE V3 LiFePo4 280Ah
Learn More
LiFePo4 cells "BetterESS Power" Battero Tech 280Ah
LiFePo4 cells "BetterESS Power" Battero Tech 280Ah
Learn More
LiFePo4 cells "BetterESS Power" EVE V3 LiFePo4 314Ah MB31
LiFePo4 cells "BetterESS Power" EVE V3 LiFePo4 314Ah MB31
Learn More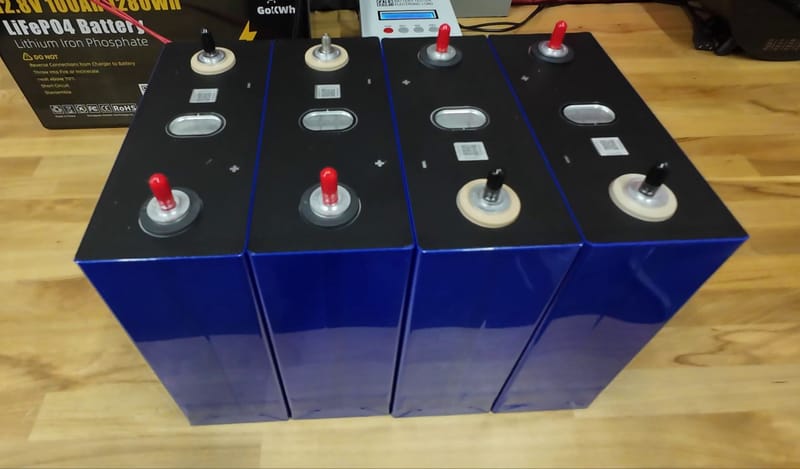
LiFePo4 cells Battero Tech "SJY Energy Direct Store"
LiFePo4 cells Battero Tech "SJY Energy Direct Store"
Learn More
LiFePo4 cells "BetterESS Power" EVE V3 LiFePo4 280Ah
LiFePo4 cells "BetterESS Power" EVE V3 LiFePo4 280Ah
Learn More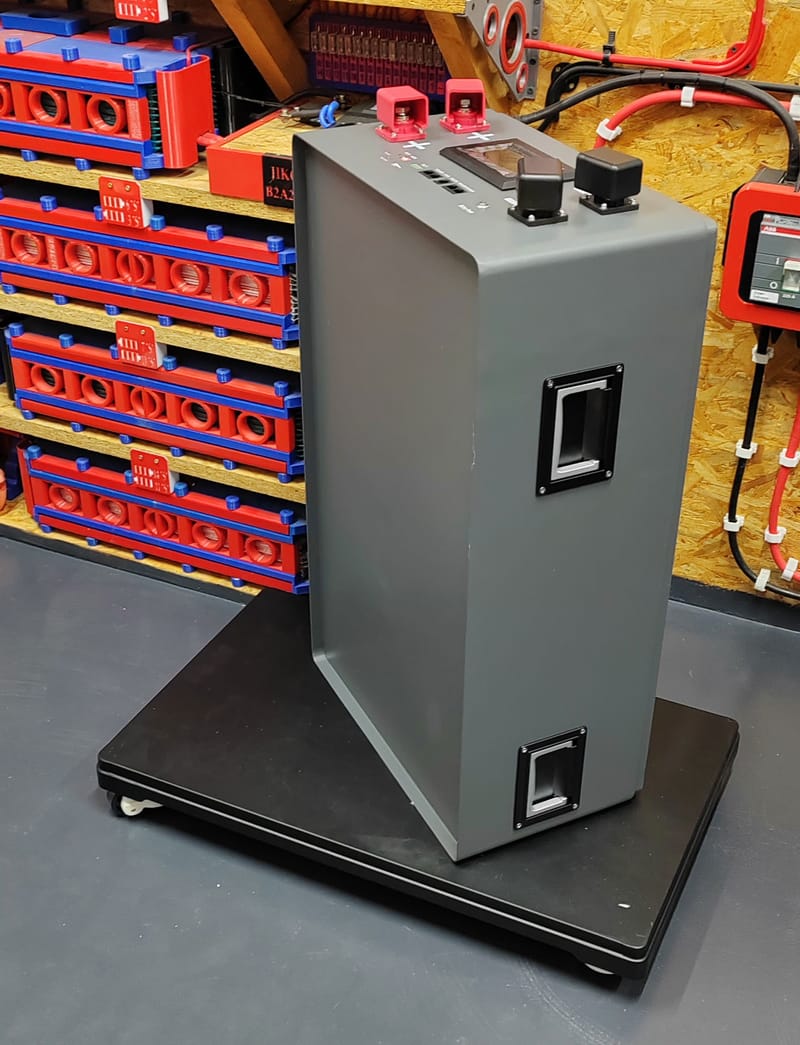
SOEC/BetterESS - LFP 280Ah Cell Housing - JKBMS
SOEC/BetterESS - LFP 280Ah Cell Housing - JKBMS
Learn More
Dongguan FENCH - LFP 280Ah Cell Housing - JKBMS
Dongguan FENCH - LFP 280Ah Cell Housing - JKBMS
Learn More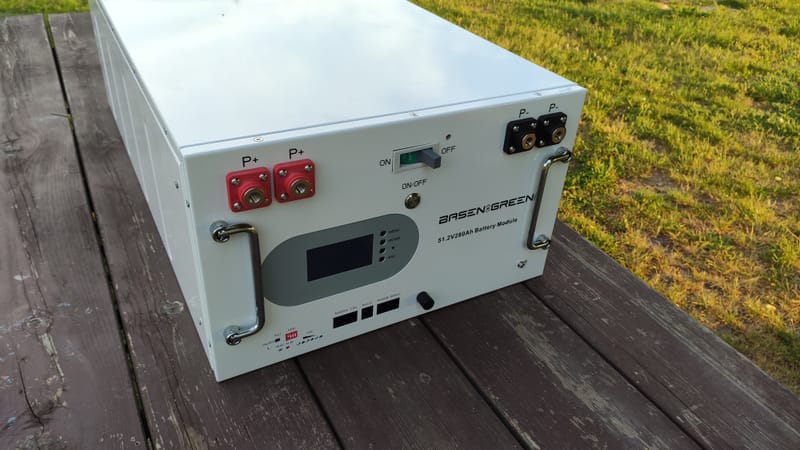
Magazyn Energii DIY - Obudowa Na Ogniwa LFP 280Ah Basen & Green
Magazyn Energii DIY - Obudowa Na Ogniwa LFP 280Ah Basen & Green
Learn More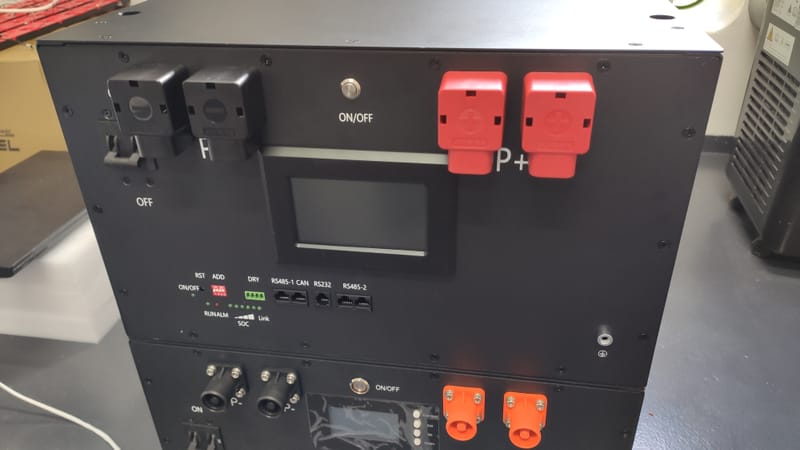
DIY Energy Storage - LFP 280Ah Cell Housing - V2 JKBMS
DIY Energy Storage - LFP 280Ah Cell Housing - V2 JKBMS
Learn More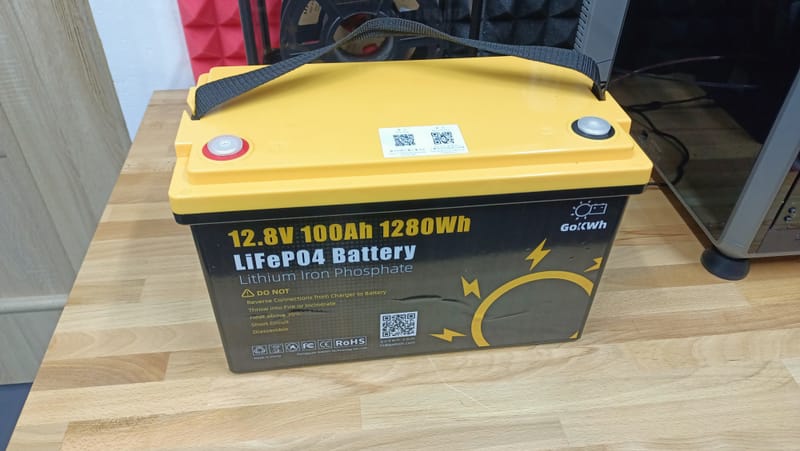
GoKWh 12V 100Ah LiFePO4 battery - Smart Bluetooth
GoKWh 12V 100Ah LiFePO4 battery - Smart Bluetooth
Learn More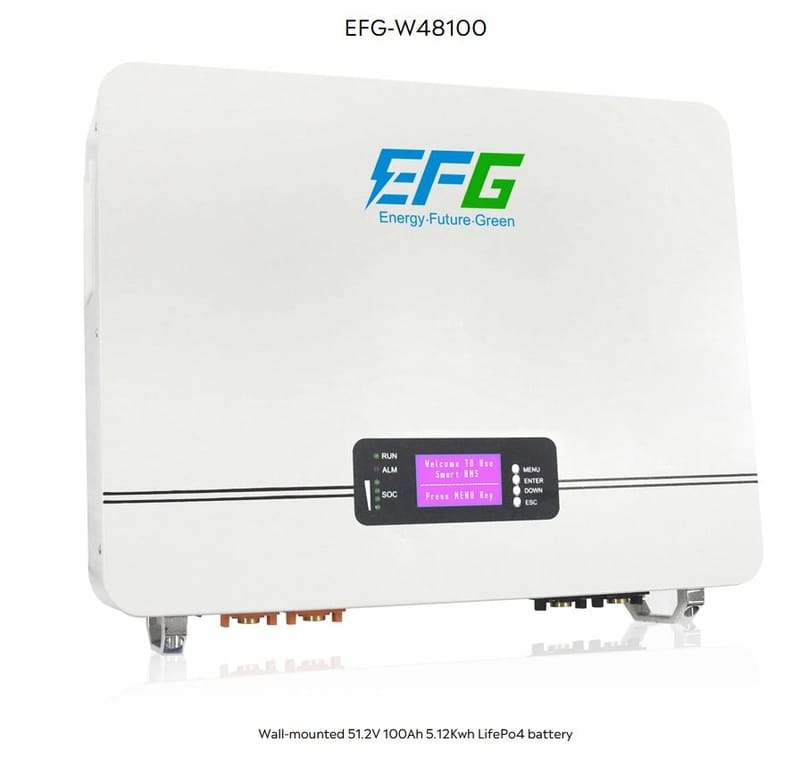
Modular Warehouse "EFG W48100" - LiFePo4 5.12kW
EFG LiFePo4 Modular Warehouse 5.12kW (Wall Mount) "EFG W48100"
Learn More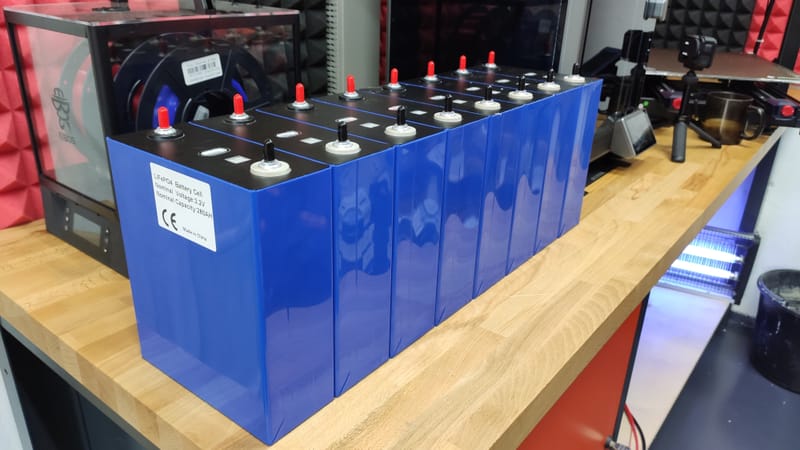
LiFePo4 cells "BetterESS" Cornex LiFePo4 280Ah
LiFePo4 cells "BetterESS" Cornex LiFePo4 280Ah
Learn More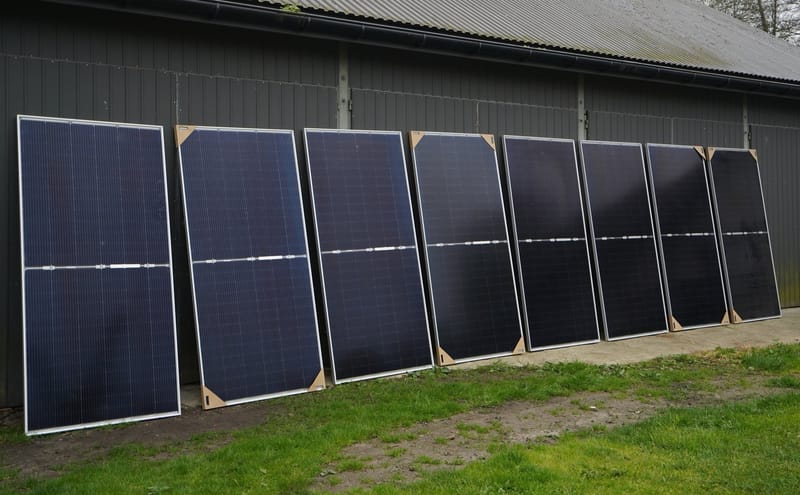
Jinko Solar Panels JKM460M-7RL3-TV (Bi-Facial)
Jinko Solar Panels JKM460M-7RL3-TV (Bi-Facial) Double-sided Panels (Bi-Facial) 460W
Learn More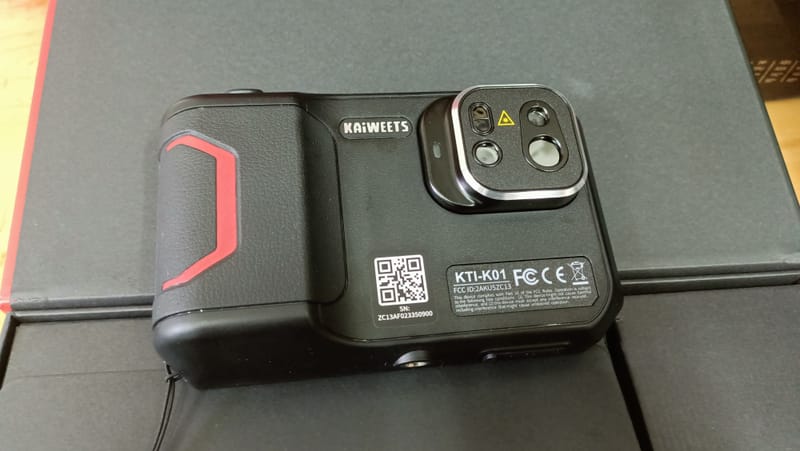
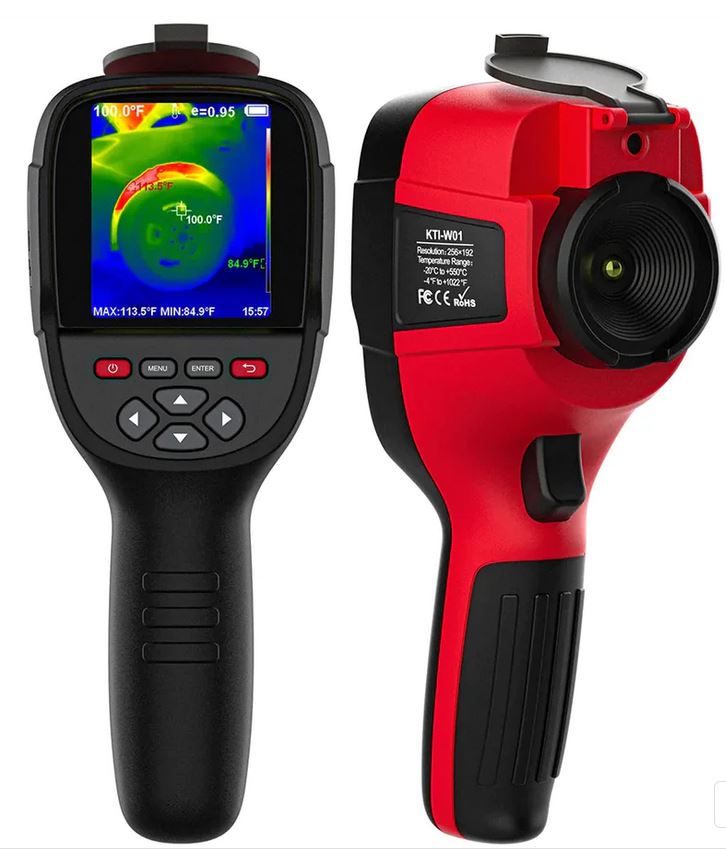
Kaiweets KTI-K01 Touch-Screen Thermal Imaging Camera
Kaiweets KTI-K01 Touch-Screen Thermal Imaging Camera
Learn More
Thermal imaging camera
Thermal Imaging Cameras, Standalone Versions and Phone Attachable Versions
Learn More
Wall-mounted heat recovery unit ZEPHYR 160 - 60m3/h WiFi
Wall-mounted heat recovery unit ZEPHYR 160 - 60m3/h WiFi
Learn More
Carplay - CarpodGo T3 Pro 60FPS Android Auto Display Screen
Carplay - CarpodGo T3 Pro 60FPS Android Auto Display Screen
Learn More
VEVOR Set of 4 leveling wheels with VEVOR GD-80S nylon wheel
VEVOR Set of 4 leveling wheels with VEVOR GD-80S nylon wheel
Learn More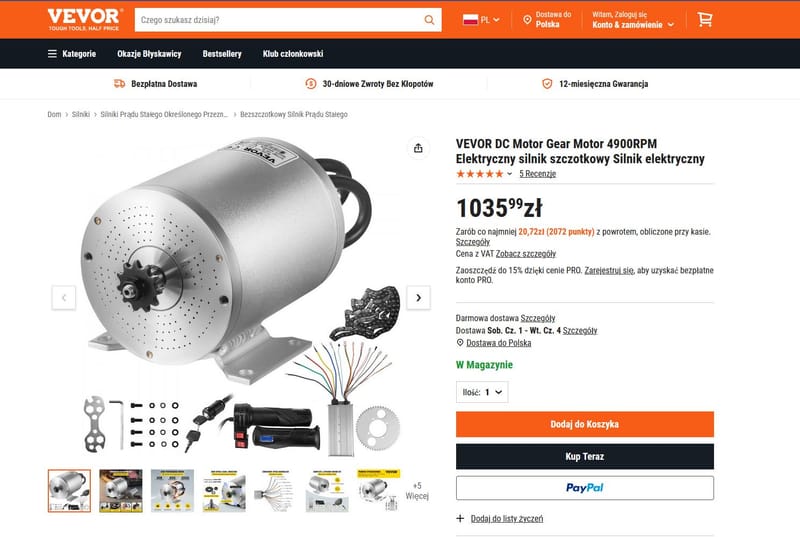
VEVOR DC 72V Motor Gear 4900RPM Electric Motor
VEVOR DC 72V Motor Gear 4900RPM Electric Motor
Learn More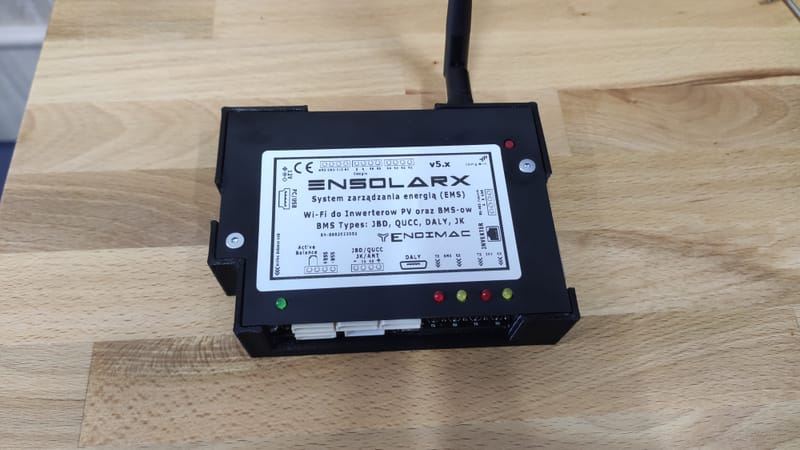
Photovoltaic and Energy Storage System Monitor - EnsolarX
Photovoltaic and Energy Storage System Monitor - EnsolarX
Learn More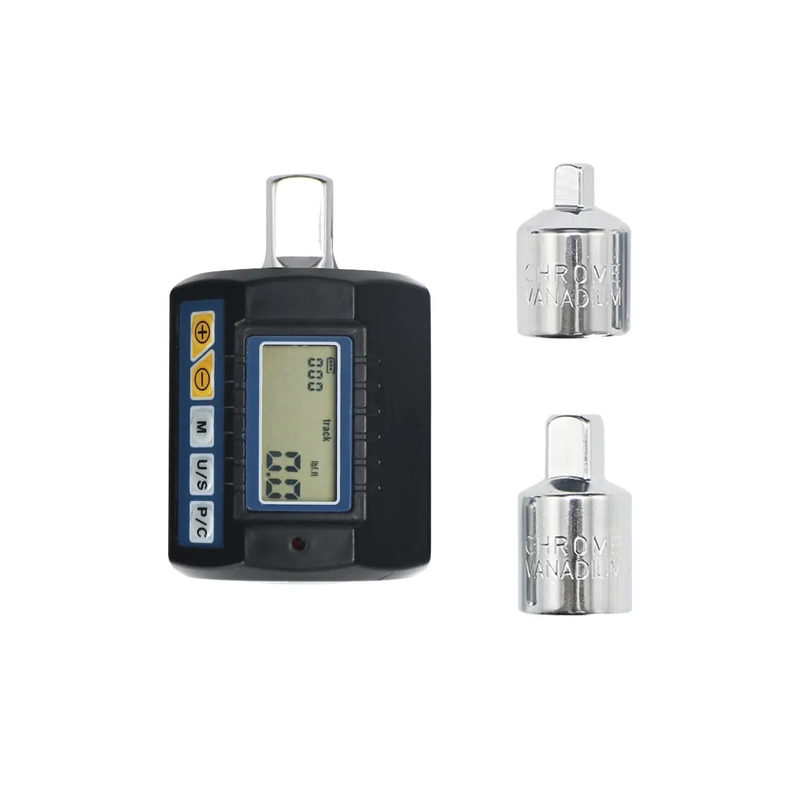
Dynanometric Attachment for the SHAHE ANC-30 Rattle
Dynanometric Attachment for the SHAHE ANC-30 Rattle
Learn More
Zemismart Tuya 3-Phase Energy Meter Zigbee/WiFi
Zemismart Tuya 3-Phase Energy Meter Zigbee/WiFi
Learn More
Zigbee Base 3 - EARU Disconnector with Energy Monitor 1-63A
Zigbee Base 3 - EARU Disconnector with Energy Monitor 1-63A
Learn More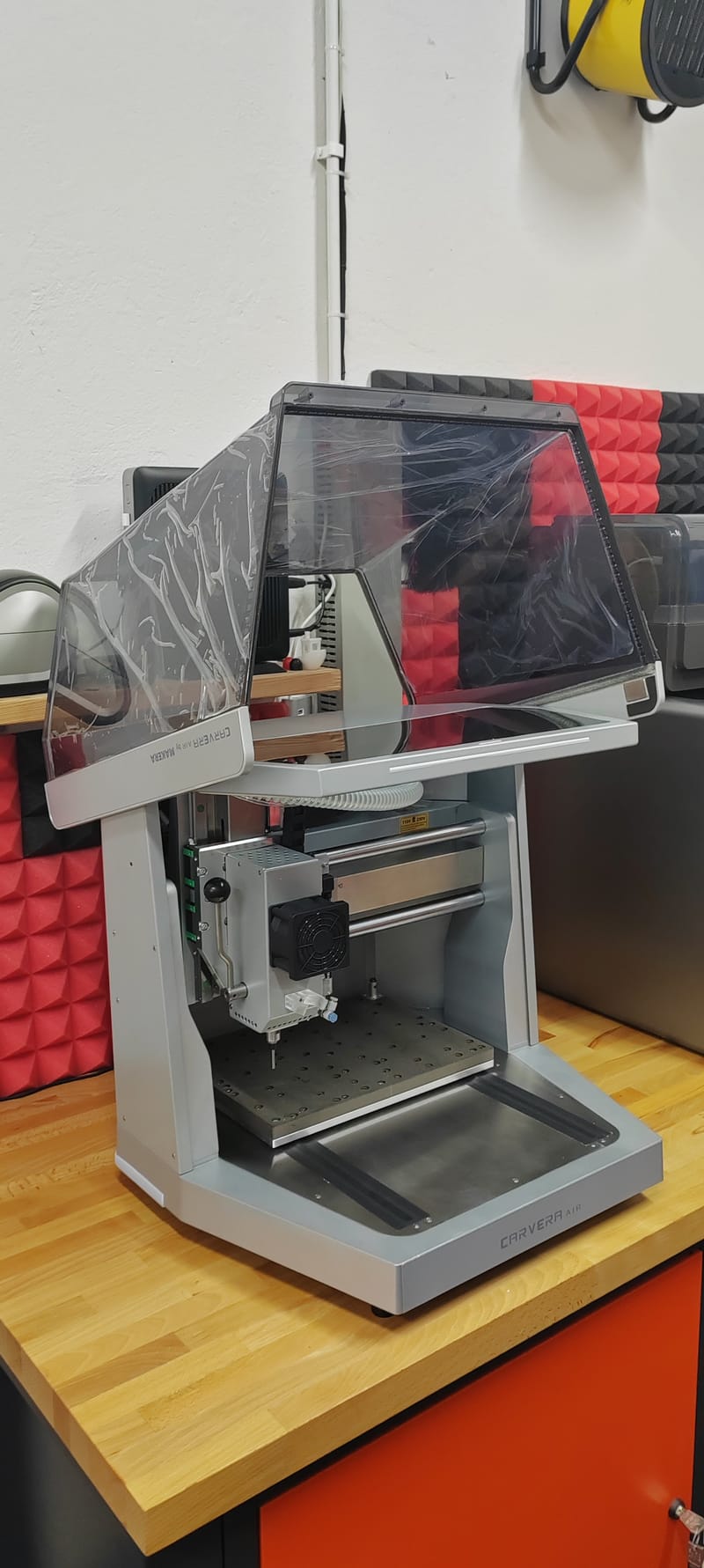
Desktop CNC Milling Machine - Makera Cavera Air
Desktop CNC Milling Machine - Makera Cavera Air
Learn More
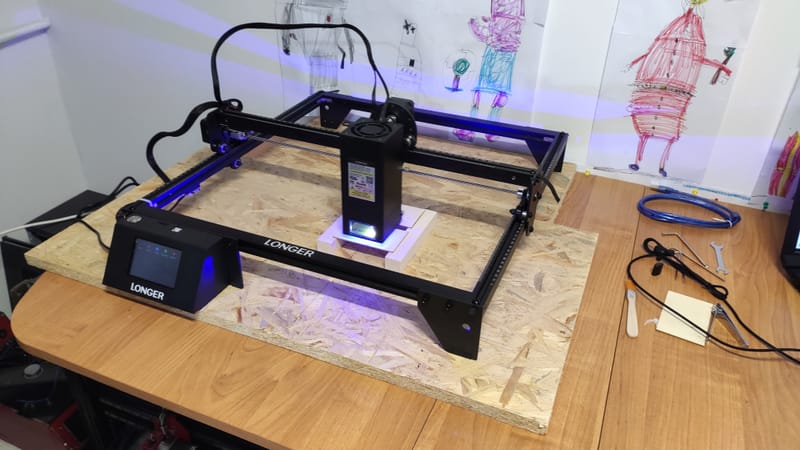
Longer Nano 6W Portable Laser, Portable Laser
Longer Nano 6W Portable Laser, Portable Laser
Learn More
Smart AlgoLaser Alpha MK2 WiFi + LCD Laser Engraver
Smart AlgoLaser Alpha MK2 WiFi + LCD Laser Engraver
Learn More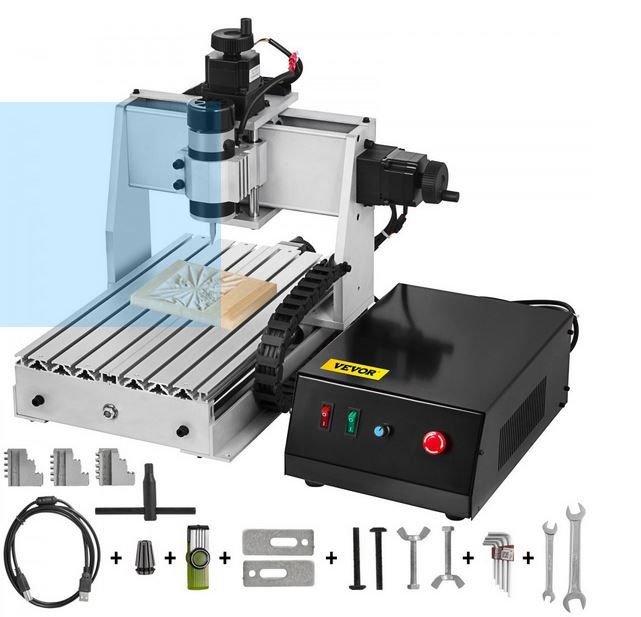
Vevor CNC 3020 3-Axis engraver/milling machine
Vevor CNC 3020 3-Axis engraver/milling machine
Learn More
Aosu SolarCam D1 Classic Kit Four Cameras + Base
Aosu SolarCam D1 Classic Kit Four Cameras + Base
Learn More
Building/Reanimating a Video/Graphics Processing Computer + CAD/CAM
Building/Reanimating a Video/Graphics Processing Computer + CAD/CAM
Learn More
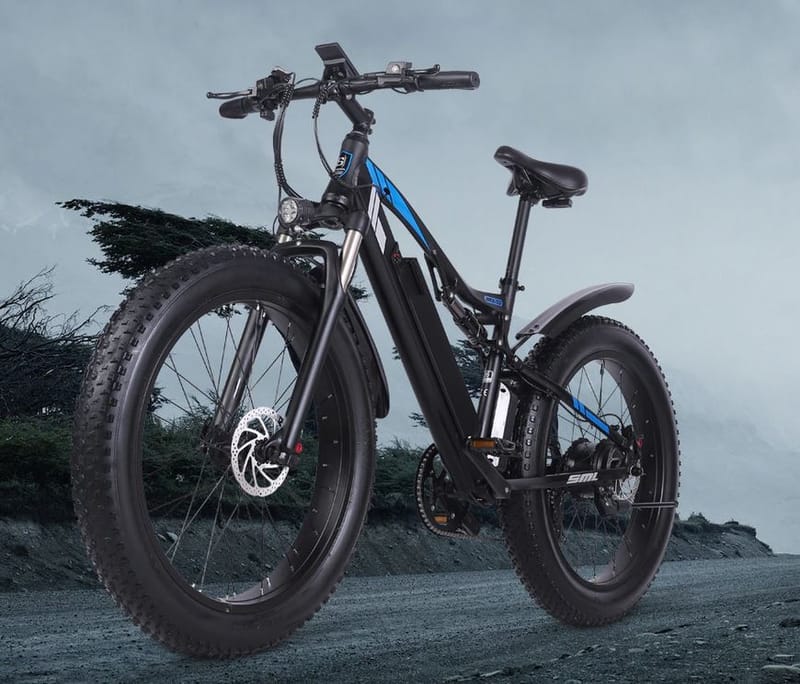
Engwe T-14 Pro Mały Rower Nie Tylko Dla Dzieci
Engwe T-14 Pro Mały Rower Nie Tylko Dla Dzieci
Learn MoreKody, Kupony i Zniżki
I'm posting a list of coupons and discounts I've worked out!
Anycubic PL
Anycubic Polish Page (PL)
Anycubic "Global"
Anycubic Global Page
Geekbuing.pl Portal
Geekbuing.pl Portal
Questions and Answers - FAQ
A base of useful knowledge in the field of Off-Grid and Energy Storage.
What are Lithium Cells/Batteries
Lithium cells consist of electrodes - an anode and a cathode - between which electricity flows. The electrodes are made of materials with different electrochemical potentials, which allows them to store and release energy. The electrolyte is responsible for the transfer of lithium ions between the electrodes during charging and discharging of the cell.
Lithium cells also have a low self-discharge, which means they maintain their energy capacity for a long period of time, even when they are not in use. In addition, lithium cells are usually readily available and easy to manufacture, making them attractive for a wide variety of applications.
It is worth remembering, however, that lithium cells require proper care and handling to ensure their safety and durability. For example, some types of lithium cells may be subject to excessive discharge, which may lead to cell damage or dangerous phenomena such as self-ignition. Therefore, it is important to follow the manufacturer's recommendations for charging and storing lithium cells.
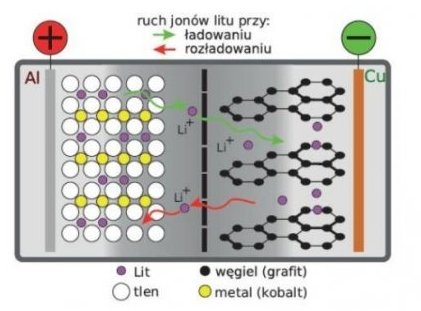
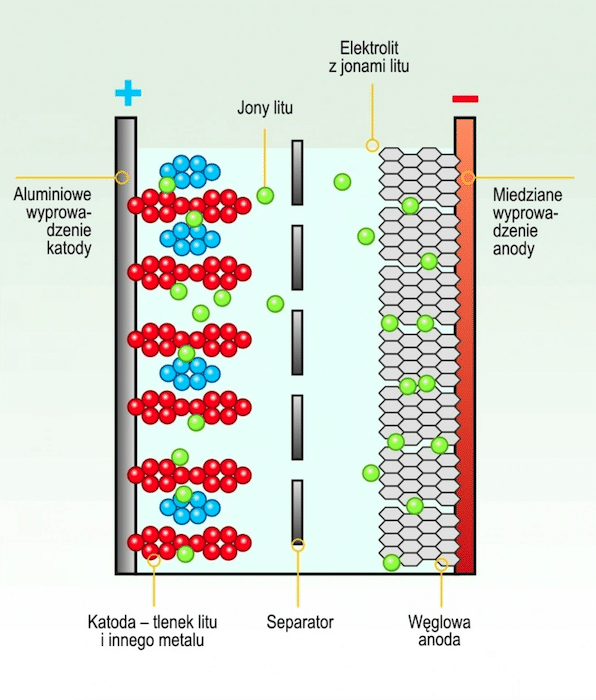
Types of Lithium Cells (Breakdown)
1. Lithium-ion (Li-ion) cellsare a type of chemical battery in which the transfer of lithium ions occurs between the anode and cathode electrodes. During charging, lithium ions move from the cathode to the anode, and during discharge, lithium ions move from the anode to the cathode. Lithium-ion cells have a high energy density, which means they deliver a lot of energy in a small area. They are commonly used in electronic devices such as laptops, smartphones and electric cars due to their high efficiency and reliability. lithium ions.
- LiCoO2 cells - with lithium anode and LiCoO2 cathode
- LiFePO4 cells - with lithium anode and LiFePO4 cathode
- LiMn2O4 cells - with lithium anode and LiMn2O4 cathode
- NMC (LiNiMnCoO2) cells - with lithium anode and LiNiMnCoO2 cathode
- NCM (LiNiCoMnO2) cells - with lithium anode and LiNiCoMnO2 cathode

2. Lithium-polymer cells (Li-Poly) are a type of lithium battery in which the electrolyte is encapsulated in a polymer matrix. Unlike traditional lithium-ion batteries, where the electrolyte is liquid, lithium-polymer batteries encapsulate the electrolyte in a plastic matrix for greater safety and flexibility. Lithium polymer cells are used in many portable devices such as smartphones, tablets and wireless headphones due to their lightness, reliability and high performance.
- Lithium-polymer cells based on electrolytic polymers (e.g. PEO and PPO polymers)
- Lithium-polymer cells based on electrolytic polymers based on compact electrolytes (e.g. electrolytic gel) Lithium-polymer cells based on nanocomposites (e.g. cells with graphene nanotubes and polymer electrolyte)

3 . Lithium metal cells (Li-Metal) are a type of lithium battery where the anode is made of pure lithium or another lithium metal. They are considered to be one of the most efficient lithium batteries because lithium is one of the most electron-capacity metals. Lithium metal cells have a high voltage, high capacity and fast charging rate. However, their use is limited by their short lifespan and the potential safety risks associated with the rapid oxidation of lithium. They are often used in high power applications such as electric cars and power tools.
- Li-Metal cells with pure lithium anode
- Li-Metal cells with lithium and other lithium metal anodes
- Li-Metal cells with lithium alloy anode

4. Lithium Carbon (Li-C) cells are a type of lithium cell that uses carbon as the anode and lithium as the cathode. In the process of charging and discharging, lithium ions move between the anode and cathode, and electrons are moved through external circuits. As a result of these processes, Li-C cells achieve a high energy density and a long lifetime of charging and discharging cycles. Li-C cells are often used in applications such as automotive batteries and energy storage systems.
These cells have a high energy density and low resistivity, making them often used in high power applications such as such as electric cars, portable electronics and energy storage. The types of lithium-carbon cells include, among others: carbon cells (LiCoO2), graphite cells (LiC6) and silicon cells (LiSi).
 5. Lithium-sulphur (Li-S) cellsare a type of lithium cell where metallic lithium is the anode and sulfur is the cathode. The electrolyte is a solution of lithium salts.
5. Lithium-sulphur (Li-S) cellsare a type of lithium cell where metallic lithium is the anode and sulfur is the cathode. The electrolyte is a solution of lithium salts.Number of Cycles - What Lithium Cells Can Do
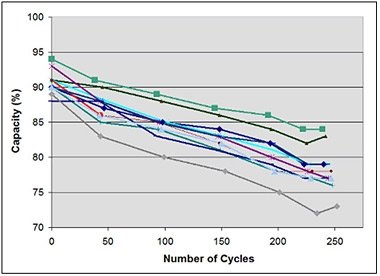
In short, this means that a given cell and the specific chemistry used in this cell will provide us with a certain number of cycles before the cell loses its parameters.
Of course, manufacturers always add a record that only under the condition of working in appropriate conditions (temperature, humidity) and with certain parameters ( current and voltage)
It is known that in practice it looks different, therefore a cell with a declared number of cycles of 500 can decorate only 100 such cycles, or it can do them equally well and 10,000,000.
What causes it and what affects the number of cycles that the cell can perform:
1. Type of cell, This is determined by the chemistry of which the cells are made, for example:
- Li-ion cells 18650 500-1000 cycles
- NCM cells 1500-2000 cycles
- LiFePo4 cells 4000-9000 cycles
- LTO cells 30 000-40 000 cycles
So, as you can see, the type of chemistry has a diametrical impact on the number of cycles, I recommend this article for exploring the topic because it is mega extensive:< br>
https: //ep.com.pl/files/11011.pdf
2. Operating Conditions, if your cells will work in conditions where the temperature will exceed that specified by the manufacturer, the life of the cells is drastically reduced.
Additionally, all versions of lithium cells (except LTO) do not tolerate charging them at temperatures below 0 Cells can be discharged even at -30 degrees, but an attempt to charge them in the cold ends with irreversible damage or loss of capacity and life.
3. Operating parameters, here we have two most important parameters:
- Intensity, each manufacturer has provided for a specific cell the recommended discharge and charging current referred to as "xC".
Where x is the capacity of the cell, to illustrate this I will write some examples, based on a cell with a capacity of 50Ah.
1C = current 50A
2C = current 100A
3C = current 150A
0.5 C = 25A current
The manufacturer provides information for a 50Ah cell that it can be charged with 0.5C (25A) current and discharged with 2C (100A) current.
Now, if we exceed these parameters, we risk premature wear of the cell, and even fire or explosion.
At the same time, it is worth adding that by maintaining much lower values than recommended by the manufacturer, we increase the safety of use of the cell, and extend its life, and instead of 500 cycles, the cell will perform more of these cycles.
- Voltage,nothing in lithium cells affects the life and safety of use. Cells that operate in a lower voltage range than those provided by the manufacturer will serve us much longer, and increase the safety of use.
Unfortunately, the disadvantage is that lowering the voltage affects the capacity of the cell, and for example, I will give a cell 18650 Li-ion:
2.5V to 4.2V = 100% capacity
2.5V to 4.1V = 90% capacity
2.5V to 4V = 80% capacity
3.35V to 4V = 70% capacity
Personally, in both my magazines I work in the range of 3.35V (because tests have shown that below this voltage the capacity is already marginal) to a maximum of 4V. As a result, my warehouse lost about 28% of its capacity in favor of itextending the service life and increasing safety.
The test performed on LG LGX E78 cells illustrates it very nicely, I invite you to familiarize yourself with my material:
https://youtu.be/2seCekWLvTM
The topic is very extensive, so I recommend see this article which explains this phenomenon very nicely,
https://batteryuniversity.com/article/bu-808-how-to-prolong-lithium-based-batteries
Can Lithium Cells Be Used in Sub-zero Temperature
Furthermore, low temperatures can also affect battery charging, particularly the charging rate. At low temperatures, chemical reactions can slow down, which can lead to lower current and longer charging times.
To avoid these problems and ensure optimal battery performance and life, it's important to follow the manufacturer's charging recommendations and discharge at sub-zero temperatures. In some cases, the manufacturer may recommend limiting the charging current or limiting the charging time to avoid excessive stress on the battery.
Also, it is worth remembering that charging the battery in sub-zero temperatures can be difficult, as the battery voltage may drop in low temperatures, which may lead to an incomplete battery charge. In these cases, it is important to use the correct charger that is rated to charge the battery in freezing temperatures, and to monitor the condition of the battery while charging to ensure it is fully charged.
Not all lithium cells can be charged in freezing temperatures. Many lithium cells have a limitation in the temperature range at which they can be charged, and some of them are not able to function at temperatures below a certain threshold. If the temperature is too low, the efficiency of the cell may decrease and there is a risk of damage to the battery.
Lithium cells operate based on a chemical reaction between the electrodes inside the battery. At lower than normal temperatures, this reaction is significantly slowed down, which can cause significant drops in battery performance. In some cases, too low a temperature can also cause crystallization of the electrolyte, which can lead to damage to the cell and its irreparable damage.
Therefore, some lithium cells are specially designed to operate in harsh conditions such as freezing temperatures, and are able to function in such conditions without damage. However, these special lithium cells are often more expensive than standard lithium cells and may have lower capacity. /strong>
Lithium Titanium (LTO) cells are often regarded as one of the most cold-resistant types of lithium cells. They can be charged at sub-zero temperatures and are often used in applications where harsh environments are required, such as electric cars and industrial equipment.
Ferro lithium phosphate (LiFePO4) cells are also considered to be resistant to low temperatures when discharging and are often used in a variety of applications, unfortunately, attempting to charge them in sub-zero temperatures causes them to be permanently and irreparably damaged.

Designations Used in Lithium Cells
SoH - State of Health - determines the general condition of the cells lithium batteries, i.e. their ability to store energy compared to their initial capacity. SoH is expressed as a percentage and is used to determine when a lithium cell needs to be replaced.
SoC - State of Charge - determines the amount of electricity a lithium cell stores in compared to its maximum capacity. SoC is also expressed as a percentage and is used to determine when lithium cells need to be charged.
DoD - Depth of Discharge - indicates the percentage of electricity that has been consumed from lithium cell in relation to its total capacity. The higher the DoD, the less energy is left in the lithium cell.
EOC - End of Life (End of Charge) is the point where a lithium cell is fully charged and no longer draws charging current . This point is important for proper charging of the lithium cell and can be detected by monitoring the voltage, temperature and/or charging current.
CC - Constant Current - is the charging mode, in which the lithium cell is charged at constant current.
CV - Constant Voltage - is a charging mode in which the lithium cell is charged at constant voltage.
strong>
C-rate - is an indicator that determines the rate of charging or discharging a lithium cell. The C-rate value is equal to the ratio of the charge/discharge current to the capacity of a lithium cell.
IR - Internal Resistance - is a measure of the internal resistance of a lithium cell. The lower the IR value, the less power loss in a lithium cell.
ESR - Equivalent Series Resistance - is the sum of the electrical resistances of all elements connected in series in a lithium cell.< br>
OCV - Open Circuit Voltage(open circuit voltage) - is the voltage generated by a lithium cell when it is not connected to any circuit.
RC - Rate Capacity (nominal capacity) - is the nominal capacity of a lithium cell, expressed in ampere-hours (Ah), which is measured under strictly defined conditions.
Ah - Ampere-hour (ampere-hour) - is a unit of measurement used to express the capacity of a lithium cell, i.e. the amount of energy it can store.
Wh - Watt-hour(Watt-hour) is a unit of electrical energy expressed in volts multiplied by ampere hours. Means the amount of energy that has been consumed or produced by a lithium cell. This is important for monitoring the power consumption and lifetime of a lithium cell.
V - Voltage (Voltage) is the potential difference between two points in an electrical circuit. Indicates the voltage level on the lithium cell and is important for monitoring the state of charge and detecting possible problems with the lithium cell.
I - Current (Current) is the amount of electrical charge that flows through a conductor in unit of time. Indicates the amount of current flowing through the lithium cell and is important for monitoring the state of charge and detecting possible problems with the lithium cell.
mΩ - For lithium cells, mΩ is the unit used to measure the internal resistance lithium cell (also called internal resistance). The internal resistance of a lithium cell is the resistance that occurs inside the cell as a result of current flowing between the cathode and the anode. This is the resistance caused by the resistance of the electrolyte and other internal components of the cell, such as electrodes and connections. Internal resistance can affect cell performance, especially when current flows through the cell during charging and discharging. The value of internal resistance is usually low, only a few millimeters, but it can vary depending on the age of the cell, temperature, charge state and other factors. Measuring the internal resistance of a lithium cell measured in milliohms can help determine cell health and cell performance.
BMS - Battery Management System is a comprehensive system that includes a management module battery and other components and features. It is responsible for monitoring the state of charge, detecting problems with the lithium cell, protecting against damage and ensuring optimal performance and durability of the lithium cell.
Balancer - in lithium cells, it is a device that ensures an even discharge of the battery lithium-ion batteries to increase performance and extend battery life. Lithium-ion cells are prone to unevenness
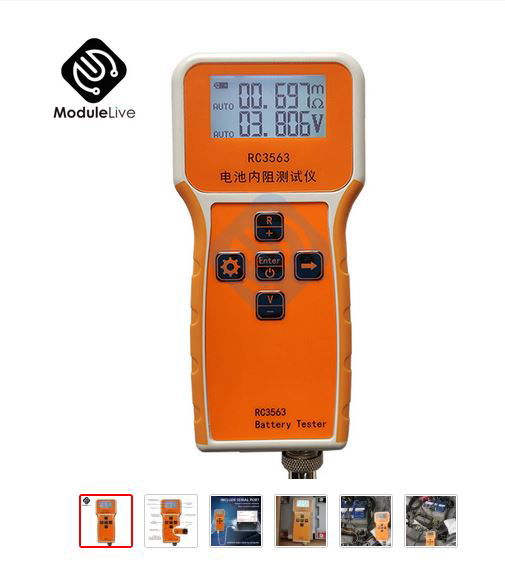
Proper IR Measurement in AC/DC Lithium Cells
--------------------------
The DC method measures the voltage drop across a lithium cell when a constant current is flowing, typically in the range of 0.1 to 1 A. The internal resistance of a lithium cell is calculated from the voltage and current drop according to Ohm's law.
The AC method consists in measuring the impedance of a lithium cell during the flow of alternating current, usually in the range from 10 Hz to 1 MHz. The impedance of a lithium cell consists of the internal resistance and the capacitance and inductance of the lithium cell. Therefore, in addition to measuring the internal resistance, the AC method can also determine other parameters of the lithium cell, such as capacitance and phase impedance.
Both methods have their advantages and disadvantages. The DC method is simple and cheap to implement, but may miss certain lithium cell problems, such as burnout of the electrodes. The AC method is more accurate and more versatile, but is more expensive and more complicated to implement.
The choice of the measurement method depends on the purpose of the measurement, the available means and the required level of measurement accuracy.
Types of Connections of Lithium Cells
- Series connection (series connection) - the fires are connected in such a way that the positive the electrodes of one cell are connected to the negative electrodes of the next cell. In this way, the voltage of the entire system increases, and the capacity depends on the capacity of a single cell.

- Parallel connection parallel connection) - the positive and negative electrodes of the cells are connected to each other in such a way that each cell is connected to the others in parallel. In this way, the capacitance of the entire system increases, and the voltage depends on the voltage of a single cell.

- Series-parallel connection ( series-parallel connection) - it is a combination of the above connections, in which groups of cells are connected in parallel and then in series. This allows you to reach a certain level of voltage and capacity.
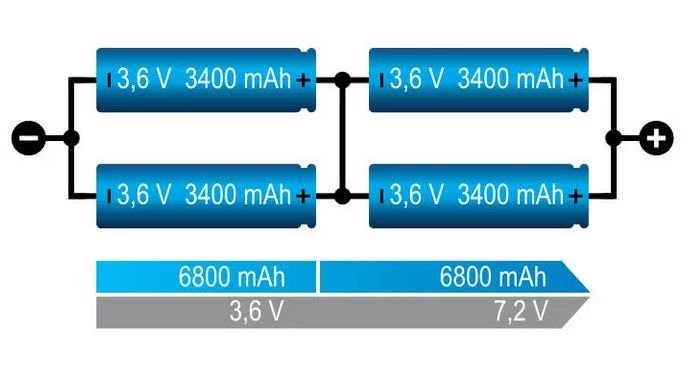
Note that series connection increases voltage but not capacitance, parallel connection increases capacity but not voltage, but connection series-parallel allows you to achieve the appropriate level of both voltage and capacitance.
Lithium Cells - Myths
Facts: Lithium cells can be charged with standard chargers available on the market, as long as they are suitable for the type of lithium cell. However, some models of lithium cells require special chargers, so it is important to check the user manual before charging.
------
2. Lithium cells have a memory effect.
Facts: Lithium cells have no memory effect, which means that they do not need to be fully discharged before recharging. In fact, frequent full discharge can shorten the life of lithium cells.
-------
3. Lithium cells cannot provide enough energy.
Facts: Lithium cells can provide enough energy to power various types of devices, including electric cars and home power systems. Their efficiency and capacity are constantly improving, which makes them more and more attractive sources of energy.
------
4. Lithium cells are dangerous and can explode.
Facts: While lithium cells may explode if damaged or overheated, they are safe for home use in most cases. The lithium cells are also designed with safety in mind, with battery management systems that prevent overheating and overvoltage.
------
5. Lithium cells are expensive to buy.
Facts: Lithium cells used to be expensive to buy, but in recent years their price has dropped significantly, making them more affordable for the average consumer. Lithium cells are also more cost-effective in the long run due to their long life and efficiency.
-------
6. Lithium cells are not suitable for use in extreme conditions.
Facts: Lithium cells are used in a variety of conditions, including extreme temperature conditions. Lithium cells are used in power systems for campsites, ships and other places where conditions are harsh. There are also lithium cells that are specially designed for extreme conditions.
-------
7 . Lithium cells must be fully discharged before storage to avoid loss of capacity.
Fact: Lithium cells should be stored approximately 50% charged to avoid loss of capacity. Long-term storage of lithium cells in a fully discharged or fully charged state can lead to damage and loss of capacity.
-------
Lithium Cells - Facts
Lithium cells have a long service life compared to other types of cells, such as lead-acid. Their performance and capacity remain stable for many years, making them more cost-effective in the long run.
------
strong>2. Lithium cells require special handling during transport.
Lithium cells require special handling during transport due to their unique construction and potential risk of explosion if damaged. Depending on the regulations in your country, there are specific requirements for transporting lithium cells.
------
3. Lithium cells are increasingly popular in automotive applications.
Lithium cells are increasingly popular in automotive applications because they offer higher efficiency and capacity than traditional cells such as lead-acid. Electric cars equipped with lithium fire are more ecological and cheaper to maintain than traditional vehicles with internal combustion engines.
-----
4. Lithium cells are greener than traditional cells.
Lithium cells are greener than traditional cells because they do not contain toxic substances such as mercury, cadmium or lead that are present in other types of cells. In addition, most of the materials used in the production of lithium cells can be recycled.
----
5. Lithium cells have a higher energy density than traditional cells.
Lithium cells have a higher energy density than traditional cells, which means they are able to store more energy in less space. This makes lithium cells more compact and lighter than traditional cells.
-----
6. Lithium cells are versatile and used in a variety of applications.
Lithium cells are used in a variety of applications, from powering portable devices to electric vehicles to power systems for homes and businesses. Due to their long life, efficiency and compactness, lithium cells are becoming more and more popular
----
Connection Types of "PV" Solar Panels
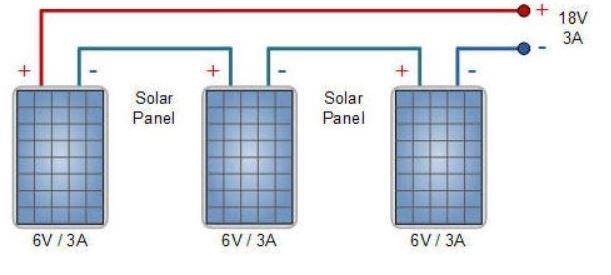


Current Mismatch of "PV" Panels
1. Series connection of PV panels and the same current-voltage characteristics.
img alt="" src="https://static.s123-cdn-static-d.com/uploads/7202780/2000_64038e4e64b23 .png" class="fr-fic fr-dii">
2. Series connection of panels with different voltage characteristics but identical current characteristics.
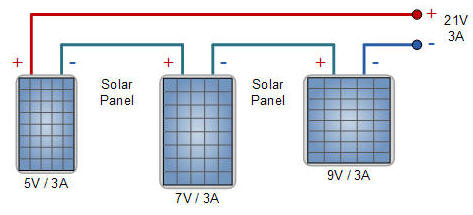
3. Series connection of panels with different current and voltage characteristics.
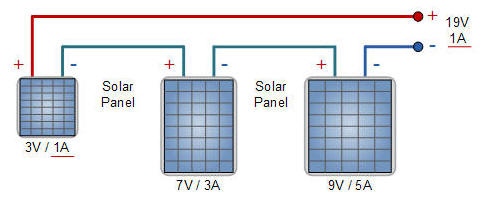
-------------
1. Parallel connection of PV panels and the same current-voltage characteristics.
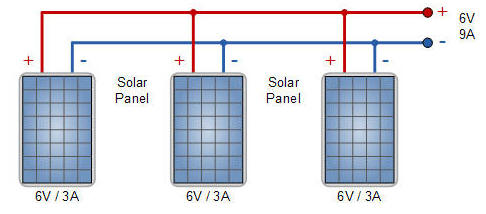
2. Parallel connection of panels with different current-voltage characteristics.
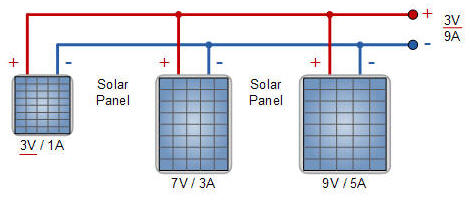
If at least one panel in the chain will have different characteristics (shading, damage, surface, etc.), the efficiency of the entire chain will be different, but in total greater than with serial connection.
--------------------------- ------------------
It follows that when it is necessary to connect different modules with different current-voltage characteristics caused by e.g.
- replacing a damaged module
- expanding the PV installation
- connecting modules from different manufacturers
- connecting modules of different sizes
Parallel connection is a more advantageous solution.
Generally, you should not:
– connect modules with different current characteristics in series
– connect modules with different voltage characteristics in parallel